Alternative Names:Meibomian gland lipogranuloma
Definition:
A chalazion is a small bump in the eyelid caused by a blockage of a tiny oil gland.
It is a cyst in the eyelid that is caused by inflammation of a blocked meibomian gland, usually on the upper eyelid.
..click to see the pictures >....…(01)..…..`(1)..…....(2)………….(3)..………………
..
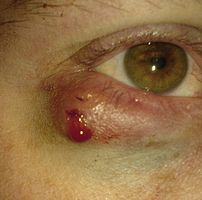
…………………………………………...Eyelid affected by Chalazion
Chalazions differ from styes (hordeolums) in that they are usually painless apart from the tenderness caused when they swell up, and in size (chalazia tend to be larger than styes). A chalazion may eventually disappear on its own after a few months, though more often than not, some treatment is necessary.
A large chalazion ca. 20 minutes upon excision. This bipartite chalazion was removed via two separate incisions. Further along the lower eyelid, signs of chronic inflammation are visible.
Causes:
A chalazion develops within the glands that produce the fluid that lubricate the eye. These are called Meibomian glands. The eyelid has approximately 100 of these glands, which are located near the eyelashes.
A chalazion is caused by blockage of the duct that drains one of these glands. A chalazion begins as swelling and tenderness, and later forms a cyst-like growth. Many chalazia disappear without treatment after a few months
Signs and symptoms:
*Painful swelling on the eyelid
*Eyelid tenderness
*Increased tearing
*Swelling on the eyelid
*Heaviness of the eyelid
Diagnosis:
Exams and Tests
Examination of eyelid confirms the diagnosis.
Rarely, the Meibomian gland duct may be blocked by a skin cancer. If this is suspected, a biopsy may be needed to diagnose the disorder.
Treatment:
A chalazion will often disappear without treatment within a month or so.
The primary treatment is application of warm compresses for 10-15 minutes at least 4 times a day. This may soften the hardened oils blocking the duct and promote drainage and healing. If the chalazion continues to get bigger, it may need to be surgically removed. This is usually done from underneath the eyelid to avoid a scar on the skin.
Topical antibiotic eye drops or ointment (eg chloramphenicol or fusidic acid) are sometimes used for the initial acute infection, but are otherwise of little value in treating a chalazion. Chalazia will often disappear without further treatment within a few months and virtually all will resorb within two years.
If they continue to enlarge or fail to settle within a few months, then smaller lesions may be injected with a corticosteroid or larger ones may be surgically removed using local anesthesia. . If the chalazion is located directly under the eyelid’s outer tissue, however, an excision from above may be more advisable so as not to inflict any unnecessary damage on the lid itself. Eyelid epidermis usually mends well, without leaving any visible traces of cicatrisation. Depending on the chalazion’s texture, the excision procedure varies: while fluid matter can easily be removed under minimal invasivion, by merely puncturing the chalazion and exerting pressure upon the surrounding tissue, hardened matter usually necessitates a larger incision, through which it can be scraped out. Any residual matter should be metabolized in the course of the subsequent healing process, generally aided by regular appliance of dry heat. The excision of larger chalazia may result in visible hematoma around the lid, which will wear off within three or four days, whereas the swelling may persist for longer. Chalazion excision is an ambulant treatment and normally does not take longer than fifteen minutes. Nevertheless, owing to the risks of infection and severe damage to the eyelid, such procedures should only be performed by a doctor.
Rarely chalazia may reoccur and these will be biopsied to help rule out tumors.
Antibiotic eye drops are usually used several days before and after removal of the cyst, but are otherwise of little value in treating a chalazion.
A chalazion that keeps coming back should be biopsied to rule out tumor.
Click for :->Chalazion and its online homeopathic treatment
Prognosis: Chalazia usually heal on their own. The outcome with treatment is usually excellent.
Complications:
A large chalazion can cause astigmatism due to pressure on the cornea. This will resolve with resolution of the chalazion.Complications including, but not limitedtohypopigmentation may occur with corticosteroid injection.The presence of recurring chalazion in the same area sometimes leads to a consideration of sebaceous cell carcinoma.The minor operation is quite painless, the eyelid is injected with a local anesthetic a clamp is put on the eyelid, then the eyelid is turned over and the chalazion is scraped out.
When to contact your Healthcare Provider:
Apply warm compresses and call your health care provider if the swelling progresses or persists longer than 1 month.
Call for an appointment with your health care provider if lumps on the eyelid continue to enlarge despite treatment or are associated with an area of eyelash loss.
Prevention:
Proper cleansing of the eyelid may prevent recurrences in people prone to chalazia. Cleaning the eyelash area with baby shampoo will help reduce clogging of the ducts.
Click to see also:-> Stye
Disclaimer: This information is not meant to be a substitute for professional medical advise or help. It is always best to consult with a Physician about serious health concerns. This information is in no way intended to diagnose or prescribe remedies.This is purely for educational purpose.
Resources:
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001006.htm
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chalazion
Related articles by Zemanta
- Chalazion Information and Treatment
- Eye Bag Surgery Philippines
- Blepharoplasty: Eyelid Reconstruction in India
- Puffy Eyes – Safe Effective Healing Treatments – Prevent Eye Puffiness and Dark Circles
- What to Do About a Chalazion That Lasts More Than a Year (brighthub.com)
- How do you treat a pustule on the corner of an eye? (zocdoc.com)
- What causes lesions to form within the eylid? (zocdoc.com)
- Antifungal Drops to Treat Blepharitis (brighthub.com)












