Definition:
Chickenpox, sometimes called varicella, is a viral infection that used to be common among young children before routine immunization. the infection, with its characteristic rash of blisters, is caused by the varicella zoster virus, which also causes herpes zoster. The virus is transmitted in airborne droplets from the coughs and sneezes of infected people or by direct contact with the blisters. You can catch chickenpox from someone with chickenpox or herpes zoster if you are not immune.
CLICK & SEE THE PICTURES
The illness is usually mild in children, but symptoms are more severe in young babies, older adolescents, and adults. chickenpox can also be more serious in people with reduced immunity, such as those with aids.
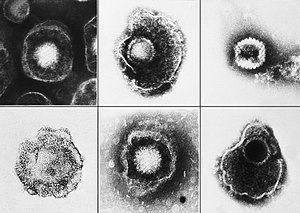
It is one of the five classical childhood exanthems or rashes, once a cause of significant morbidity and mortality, but now chiefly of historical importance. Formerly one of the childhood infectious diseases caught by and survived by almost every child, its incidence had been reduced since the introduction and use of a varicella vaccine in 1995 in the U.S. and Canada to inoculate against the disease. Areas such as England, where the vaccine is not mandated, have increasing prevalence rates for chickenpox. Chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), also known as human herpes virus 3 (HHV-3), one of the eight herpes viruses known to affect humans. It starts with conjunctival and catarrhal symptoms and then characteristic spots appearing in two or three waves, mainly on the body and head rather than the hands and becoming itchy raw pox (pocks), small open sores which heal mostly without scarring.
Chickenpox has a 10-21 day incubation period and is highly contagious through physical contact two days before symptoms appear. Following primary infection there is usually lifelong protective immunity from further episodes of chickenpox.
Chickenpox is rarely fatal (usually from varicella pneumonia), with pregnant women and those with a suppressed immune system being more at risk. Pregnant women not known to be immune and who come into contact with chickenpox may need urgent treatment as the virus can cause serious problems for the fetus. This is less of an issue after 20 weeks.
The most common complication of chicken pox is shingles; this is most frequently a late effect.
Causes:
In a typical scenario, a young child is covered in pox and out of school for a week. The first half of the week the child feels miserable from intense itching; the second half from boredom. Since the introduction of the chickenpox vaccine, classic chickenpox is much less common.
Chickenpox is extremely contagious, and can be spread by direct contact, droplet transmission, and airborne transmission. Even those with mild illness after the vaccine may be contagious
Signs and symptoms:
The symptoms of chickenpox appear 1-3 weeks after infection. In children, the illness often starts with a mild fever or headache; in adults, there may be more pronounced flulike symptoms. as infection with the virus progresses, the following symptoms usually become apparent:
· Rash in the form of crops of tiny red spots that rapidly turn into itchy, fluid-filled blisters. within 24 hours the blisters dry out, forming scabs. successive crops occur for 1-6 days. The rash may be widespread or consist of only a few spots, and it can occur anywhere on the head or body.
· Sometimes, discomfort during eating caused by spots in the mouth that have developed into ulcers.
A person is contagious from about 2 days before the rash first appears until it crusts over it about 10-14 days.
Itis a highly contagious disease that spreads from person to person by direct contact or through the air from an infected person’s coughing or sneezing. Touching the fluid from a chickenpox blister can also spread the disease. A person with chickenpox is contagious from one to two days before the rash appears until all blisters have formed scabs. This may take five to 10 days. It takes from 10-21 days after contact with an infected person for someone to develop chickenpox.
The chickenpox lesions (blisters) start as a two to four millimeter red papule which develops an irregular outline (a rose petal). A thin-walled, clear vesicle (dew drop) develops on top of the area of redness. This “dew drop on a rose petal” lesion is very characteristic for chickenpox. After about eight to 12 hours the fluid in the vesicle gets cloudy and the vesicle breaks leaving a crust. The fluid is highly contagious, but once the lesion crusts over, it is not considered contagious. The crust usually falls off after seven days sometimes leaving a crater-like scar. Although one lesion goes through this complete cycle in about seven days, another hallmark of chickenpox is the fact that new lesions crop up every day for several days. Therefore, it may take about a week until new lesions stop appearing and existing lesions crust over. Children are not to be sent back to school until all lesions have crusted over.
Chickenpox is highly contagious and is spread through the air when infected people cough or sneeze, or through physical contact with fluid from lesions on the skin. Zoster, also known as shingles, is a reactivation of chickenpox and may also be a source of the virus for susceptible children and adults. It is not necessary to have physical contact with the infected person for the disease to spread. Those infected can spread chickenpox before they know they have the disease – even before any rash develops. In fact, people with chickenpox can infect others from about two days before the rash develops until all the sores have crusted over, usually four to five days after the rash starts.
Possible Complications:
*Women who get chickenpox during pregnancy are at risk for congenital infection of the fetus.
*Newborns are at risk for severe infection, if they are exposed and their mothers are not immune.
*A secondary infection of the blisters may occur.
*Encephalitis is a serious, but rare complication.
*Reye’s syndrome, pneumonia, myocarditis, and transient arthritis are other possible complications of chickenpox
*Cerebellar ataxia may appear during the recovery phase or later. This is characterized by a very unsteady walk.
The most common complication of chickenpox is bacterial infection of the blisters due to scratching. other complications include pneumonia, which is more common in adults, and rarely inflammation of the brain. newborn babies and people with reduced immunity are at higher risk of complications. Rarely, if a woman develops chickenpox in early pregnancy, the infection may result in fetal abnormalities.
Later in life, chickenpox viruses remaining dormant in the nerves can reactivate, causing shingles.
Secondary infections, such as inflammation of the brain, can occur in immunocompromised individuals. This is more dangerous with shingles.
Congenital defects in babies:
These may occur if the child’s mother was exposed to the zoster virus during pregnancy. Effects on the fetus may be minimal in nature but physical deformities range in severity from under developed toes and fingers, to severe anal and bladder malformation. Possible problems include:
*Damage to brain: encephalitis, microcephaly, hydrocephaly, aplasia of brain
*Damage to the eye (optic stalk, optic cap, and lens vesicles), microphthalmia, cataracts, chorioretinitis, optic atrophy
*Other neurological disorder: damage to cervical and lumbosacral spinal cord, motor/sensory deficits, absent deep tendon reflexes, anisocoria/Horner’s syndrome
*Damage to body: hypoplasia of upper/lower extremities, anal and bladder sphincter dysfunction
*Skin disorders: (cicatricial) skin lesions, hypopigmentation
Diagnosis:
Chickenpox can usually be diagnosed from the appearance of the rash. Children with mild infections do not need to see a doctor, and rest and simple measures to reduce fever are all that are needed for a full recovery. calamine lotion may help relieve itching. To prevent skin infections, keep fingernails short and avoid scratching. people at risk of severe attacks, such as babies, older adolescents, adults, and people with reduced immunity, should see their doctor immediately. An antiviral drug may be given to limit the effect of the infection, but it must be taken in the early stages of the illness in order to be effective.
Prognosis and treatment:
Children who are otherwise healthy usually recover within 10-14 days from the onset of the rash, but they may have permanent scars where blisters have become infected with bacteria and then been scratched. Adolescents, adults, and people with reduced immunity take longer to recover from chickenpox.
Chickenpox infection tends to be milder the younger a child is and symptomatic treatment, with a little sodium bicarbonate in baths or antihistamine medication to ease itching, and paracetamol (acetaminophen) to reduce fever, are widely used. Ibuprofen can also be used on advice of a doctor. However, aspirin or products containing aspirin must not be given to children with chickenpox (or any fever-causing illness), as this risks causing the serious and potentially fatal Reye’s Syndrome.
There is no evidence to support the effectiveness of topical application of calamine lotion, a topical barrier preparation containing zinc oxide in spite of its wide usage and excellent safety profile.
It is important to maintain good hygiene and daily cleaning of skin with warm water to avoid secondary bacterial infection. Infection in otherwise healthy adults tends to be more severe and active; treatment with antiviral drugs (e.g. acyclovir) is generally advised. Patients of any age with depressed immune systems or extensive eczema are at risk of more severe disease and should also be treated with antiviral medication. In the U.S., 55 percent of chickenpox deaths are in the over-20 age group, even though they are a tiny fraction of the cases.
In most cases, it is enough to keep children comfortable while their own bodies fight the illness. Oatmeal baths in lukewarm water provide a crusty, comforting coating on the skin. An oral antihistamine can help to ease the itching, as can topical lotions. Lotions containing antihistamines are not proven more effective. Trim the fingernails short to reduce secondary infections and scarring.
Safe antiviral medicines have been developed. To be effective, they usually must be started within the first 24 hours of the rash. For most otherwise healthy children, the benefits of these medicines may not outweigh the costs. Adults and teens, at risk for more severe symptoms, may benefit if the case is seen early in its course
In addition, for those with skin conditions (such as eczema or recent sunburn), lung conditions (such as asthma), or those who have recently taken steroids, the antiviral medicines may be very important. The same is also true for adolescents and children who must take aspirin on an ongoing basis.
Some doctors also give antiviral medicines to people in the same household who subsequently come down with chickenpox. Because of their increased exposure, they would normally experience a more severe case of chickenpox.
DO NOT USE ASPIRIN for someone who may have chickenpox. Use of aspirin has been associated with Reyes Syndrome. Ibuprofen has been associated with more severe secondary infections. Acetaminophen may be used.
Click for Ayurvedic medication of Chickenpox….…(1).…….(2)……..(3).…..(4)
Click for Homeopathic Remedies of Chicken Pox …….(1).…..(2).…..(3)..…..(4)
Prevention:
Once you catch chickenpox, the virus usually stays in your body forever. You probably will not get chickenpox again, but the virus can cause shingles in adults. A chickenpox vaccine can help prevent most cases of chickenpox, or make it less severe if you do get it.
One attack of chickenpox gives lifelong immunity to the disease. However, the varicella zoster virus remains dormant within nerve cells and may reactivate years later, causing herpes zoster. Immunization against chickenpox is now routine for babies aged 12-18 months and is recommended for children aged 11-12 years who have neither had chickenpox nor been immunized.
Vaccination:
A varicella vaccine has been available since 1995 to inoculate against the disease. Some countries require the varicella vaccination or an exemption before entering elementary school. Protection is not lifelong and further vaccination is necessary five years after the initial immunization.
In the UK, varicella antibodies are measured as part of the routine of prenatal care, and by 2005 all NHS healthcare personnel had determined their immunity and been immunised if they were non-immune and have direct patient contact. Population-based immunization against varicella is not otherwise practiced in the UK, because of lack of evidence of lasting efficacy or public health benefit.
Vaccination reactions:
Common and mild reactions following vaccination may include:
*Fever of 101.9 (38.9 C) up to 42 days after injection
*Soreness, itching at the site of injection within 2 days
*Rash occurring at site of injection anywhere form 8 to 19 days after injection. If this happens you are considered contagious.
*Rash on other parts of body anywhere from 5 to 26 days after injection. If this happens you are considered contagious.
Fever and discomfort may be lessened by taking medication containing paracetamol (aka acetaminophen, such as Panadol, Tempra, Tylenol) or ibuprofen.
CLICK TO READ
Disclaimer: This information is not meant to be a substitute for professional medical advise or help. It is always best to consult with a Physician about serious health concerns. This information is in no way intended to diagnose or prescribe remedies.This is purely for educational purpose.
Resources:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chickenpox
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001592.htm
http://www.charak.com/DiseasePage.asp?thx=1&id=117
![Reblog this post [with Zemanta]](https://i0.wp.com/img.zemanta.com/reblog_e.png?w=580)