Alternative Names:Repetitive stress injury, Repetitive motion injuries, Repetitive motion disorder (RMD), Cumulative trauma disorder (CT), Occupational overuse syndrome, Overuse syndrome, Regional musculoskeletal disorder
Definition:
Repetitive strain injury (RSI) is an injury of the musculoskeletal and nervous systems that may be caused by repetitive tasks, forceful exertions, vibrations, mechanical compression (pressing against hard surfaces), or sustained or awkward positions.
The term “repetitive strain injury” is most commonly used to refer to patients in whom there is no discrete, objective, pathophysiology that corresponds with the pain complaints. It may also be used as an umbrella term incorporating other discrete diagnoses that have (intuitively but often without proof) been associated with activity-related arm pain such as carpal tunnel syndrome, cubital tunnel syndrome, thoracic outlet syndrome, DeQuervain’s syndrome, stenosing tenosynovitis/trigger finger/thumb, intersection syndrome, golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylosis), tennis elbow (lateral epicondylosis), and focal dystonia.
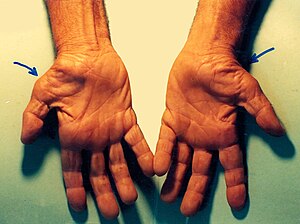
click to see pictures…..(0)....(1).…...(2)….….(3)
Finally RSI is also used as an alternative or an umbrella term for other non-specific illnesses or general terms defined in part by unverifiable pathology such as reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome (RSDS), Blackberry thumb, disputed thoracic outlet syndrome, radial tunnel syndrome, “gamer’s thumb” (a slight swelling of the thumb caused by excessive use of a gamepad), “Rubik’s wrist” or “cuber’s thumb” (tendinitis, carpal tunnel syndrome, or other ailments associated with repetitive use of a Rubik’s Cube for speedcubing), “stylus finger” (swelling of the hand caused by repetitive use of mobile devices and mobile device testing.), “raver’s wrist”, caused by repeated rotation of the hands for many hours (for example while holding glow sticks during a rave).
Although tendinitis and tenosynovitis are discrete pathophysiological processes, one must be careful because they are also terms that doctors often use to refer to non-specific or medically unexplained pain, which they theorize may be caused by the aforementioned processes.
Doctors have also begun making a distinction between tendinitis and tendinosis in RSI injuries. There are significant differences in treatment between the two, for instance in the use of anti-inflammatory medicines, but they often present similar symptoms at first glance and so can easily be confused.
Types of RSIs that affect computer users may include non-specific arm pain or work related upper limb disorder (WRULD). Conditions such as RSI tend to be associated with both physical and psychosocial stressors.
Symptoms:
The following complaints are typical in patients who might receive a diagnosis of RSI:
*Short bursts of excruciating pain in the arm, back, shoulders, wrists, hands, or thumbs (typically diffuse – i.e. spread over many areas).
*The pain is worse with activity.
*Weakness, lack of endurance.
In contrast to carpal tunnel syndrome, the symptoms tend to be diffuse and non-anatomical, crossing the distribution of nerves, tendons, etc. They tend not to be characteristic of any discrete pathological condition.
1.The users experience constant pain in the hands, elbows, shoulders, neck, and the back. Other symptoms of Repetitive Stain Injury are cramps, tingling, and numbness in the hands. The hand movements of the user may become clumsy and the person may find it difficult even to fasten buttons.
2.Another variant of Repetitive Strain Injury is that, it may produce painful symptoms in the upper limbs, but the site may be difficult to locate.
3.The common diagnoses seen in Repetitive Strain Injury are Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, Tenosynovitis, Bursitis, White Limb, and Shoulder pain. A major cause is due to long unbroken periods of work. Ergonomics or the lack of it plays a very important role. Lack of information about the condition leads to neglect by the concerned individuals.
Frequency :A 2008 study showed that 68% of UK workers suffered from some sort of RSI, with the most common problem areas being the back, shoulders, wrists, and hands.
Physical examination and diagnostic testing; The physical examination discloses only tenderness and diminished performance on effort-based tests such as grip and pinch strength—no other objective abnormalities are present. Diagnostic tests (radiological, electrophysiological, etc.) are normal. In short, RSI is best understood as an apparently healthy arm that hurts. Whether there is currently undetectable damage remains to be established.
Causes:
RSI is believed by many to be caused due to lifestyle without ergonomic care, E.g. While working in front of computers, driving, traveling etc. Simple reasons like ‘Using a blunt knife for everyday chopping of vegetables’, may cause RSI.
Repetitive Strain Injury occurs when the movable parts of the limbs are injured. Repetitive Strain Injury usually caused due to repetitive tasks, incorrect posture, stress and bad ergonomics. Repetitive Strain Injury generally causes numbness, tingling, weakness, stiffing, and swelling and even nerve damage. The chief complaint is the constant pain in the upper limbs, neck, shoulder and back.
The main cause of this main are the repetitive activities, forceful activities of arms and hand and awkward postures. The other causes of Repetitive Strain Injuries are sitting in a fixed posture and poor workplace ergonomics.
Other typical habits that some sources believe lead to RSI
*Reading or doing tasks for extended periods of time while looking down.
*Sleeping on an inadequate bed/mattress or sitting in a bad armchair and/or in an uncomfortable position.
*Carrying heavy items.
*Holding one’s phone between neck and shoulder.
*Watching TV in incorrect position e.g. Too much to the left/right.
*Sleeping with head forward, while traveling.
*Prolonged use of the hands, wrists, back, neck, etc.
*Sitting in the same position for a long period of time.
Diagnosis:
Repetitive task and stress affects the body parts causes RSI. An instance of this is using a screwdriver, if you keep using the screwdriver without a break, you feel your wrist become restricted and you feel pain and you may also experience the loss of movement. This is the initial stage of RSI.
RSI, or should we say the group of syndromes that make up repetitive strain injury only affects the back, neck and arms. A lot of people without even realizing may suffer with RSI.
You may have had pains in your wrists or arms that you explained as being tired if you are working on an assembly line or you’re an avid musician who can’t put their guitar down. These pains are more than likely the initial RSI symptoms.
Judging the Symptom:
The problem in diagnosing repetitive strain injury is the fact that is can be hard to judge the symptoms, after all RSI is just a name given to a group of different conditions that are all related in some way to the affects we attribute to RSI.
Not only do we have this issue, we also have the problem that some of the symptoms related with repetitive strain injury are found in other, more dangerous conditions such as angina.
Even though RSI only affects the upper torso and limbs, the symptoms can in fact appear in the lower half of the body; this is due to the vertebral nerves that can be affected in some cases so the pains appear in the legs.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is the most common out of all the syndromes that make up the condition called RSI.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that affects the median nerve situated in the carpal canal in the wrist, when the same movement is carried out frequently it can cause the tendons also situated in the carpal canal to become inflamed and compress the nerve causing pain and tightness causing loss of movement.
The most famous out of all the syndromes that make up repetitive stress injury is carpal tunnel syndrome because it affects a lot of people who spend long periods on the computer without supporting their wrists appropriately.
Other Conditions:
There are some conditions that the every day layman may be aware of golfers elbow, which is called medial epicondylitis, or like tennis elbow, which is officially called lateral epicondylitis.
You should visit your doctor if you suffer with pains, aches, stiffness, numbness or tingling sensations in your back, arms, wrists or hands. While RSI is not life threatening it can affect you more than you think.
Eventually without visiting a medical professional the symptoms can become ever worse, or you may even find the RSI could be something more risky. Learn more about ergonomics at safecomputingtips.com.
Most common and simple measure of treatment, which is more common sense than anything is painkillers and anti inflammatory pills, these are available over the counter at any good pharmacy.When taking painkillers and anti inflammatory pills it is important that you rest the affected area, just because the pain is not there it doesn’t mean the condition has instantly been resolved.Another simple measure is speaking to your employer, you may find they have guidelines to work towards that may mean you can get some support in alleviating your condition. This means your work place may be assessed and improvements implemented.You can get a simple support bandage from your local pharmacy to help add strength to the affected area, if it is your wrist or arm. You may need to purchase a special keyboard and/or mouse or get speech recognition software in order to prevent further irritation to your injury.Speech recognition software is a great alternative for those who suffer due to computer work, speech recognition software works by the software writing what you say for you.Your medical professional might possibly prescribe that you wear an orthopedic hand brace. You don’t want to wear one of these if your doctor doesn’t. it because it could lead to further injury.Therapy:Your doctor may prescribe physical therapy, a physical therapists role is to develop and maximize the movement of the body, and this can also include the provision of aids to alleviate symptoms.
Another prescribed therapy your doctor may request is occupational therapy, it may sound like occupational therapy and physical therapy are very similar but there are differences.
Occupational therapy helps develop and maintain the skills required to carry out all the general functions needed to live a comfortable life.
Occupational therapy includes assessing what a persons requirements are and supporting them with offering recommendations on adapting to their living or working space and offering simple exercises to regain movement.
Alternative Treatment:
Deep body massages have been reported to work wonders for those suffering with repetitive strain injury as it works deep into the body’s soft tissues like the muscles and tendons where the pain comes from.
Soft tissue therapy is a type of therapy that works by decompressing the area surrounding the RSI. This will increase your circulation and aid in healing. They may also try biofeedback. This is generally used to reduce tension in the muscles in your shoulders and neck.
Some people have reported that slow martial arts like Tai Chi can have a dramatic affect on their condition because they work on specific movements and improve strength and flexibility.
Surjury:
As a last resort, the medical professional might recommend to have surgery. one should keep in mind that it doesn’t always work and he or she will be left without the use of one’s hand and arm for a long time. The above treatment methods have been proven to help heal even the worst types of RSI disorders when they are done correctly.
You may click to see the using of modern ergonomics in home office
Exercise:
Exercise decreases the risk of developing RSI.
*Doctors sometimes recommend that RSI sufferers engage in specific strengthening exercises, for example to improve posture.
*In light of the fact that a lifestyle that involves sitting at a computer for extended periods of time increases the probability that an individual will develop excessive kyphosis, theoretically the same exercises that are prescribed for thoracic outlet syndrome or kyphotic postural correction would benefit an RSI sufferer.
*Some sources[who?] recommend motoric exercises and ergo-aerobics to decrease chances of strain injury. Ergo-aerobics target touch typists and people who often use computer keyboard.
Resuming normal activities despite the pain:
Psychologists Tobias Lundgren and Joanne Dahl have asserted that, for the most difficult chronic RSI cases, the pain itself becomes less of a problem than the disruption to the patient’s life caused by
*avoidance of pain-causing activities
*the amount of time spent on treatment
They claim greater success from teaching patients psychological strategies for accepting the pain as an ongoing fact of life, enabling them to cautiously resume many day-to-day activities and focus on aspects of life other than RSI
Psychosocial factors:
Studies have related RSI and other upper extremity complaints with psychological and social factors. A large amount of psychological distress showed doubled risk of the reported pain, while job demands, poor support from colleagues, and work dissatisfaction also showed an increase in pain, even after short term exposure.
For example, the association of Carpal tunnel syndrome with arm use is commonly assumed but not well-established. Typing has long been thought to be the cause of carpal tunnel syndrome, but recent evidence suggests that, if anything, typing may be protective. Another study claimed that the primary risk factors for Carpal tunnel syndrome were “being a woman of menopausal age, obesity or lack of fitness, diabetes or having a family history of diabetes, osteoarthritis of the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb, smoking, and lifetime alcohol intake.
Prevention:
Risk of RSI can be reduced a lot by warming up and cooling down the muscles used, taking regular breaks throughout the day, having an appropriate workstation and seating position, and practising relaxation. If the job puts one at risk of RSI he or she should seek out expert advice on prevention from your employer or professional body.
Repetitive Stress Injury symptoms when found, people should seek medical attention as early as possible. Measures that can be adopted to avoid Repetitive Stress Injury at an individual level include:
Position: The recommended position to sit in front of a computer is semi-reclined with the forearms resting in a cradle or on an extension of the keyboard support to prevent Repetitive Stress Injury.
There should be ample support for the back. The hands should be free and point in the direction of the forearms. The feet should rest on the ground or feet support. The distance of the monitor should be 18 inches or more and at a slightly lower level than the eye level. Using these measures Repetitive Stress Injury caused out of position can be avoided.
Hydration: The Repetitive Stress Injury can be prevented by drinking adequate fluids to keep the tendons and soft- tissues soft.
Shortcuts: Using keyboard shortcuts and less of mouse is the most effective preventive method to avoid Repetitive Stress Injury. Touch the ergonomic keyboard softly and do not pound at it. The wrist should rest on the table or wrist rest.
Telephone use: Don’t cradle the telephone between the face and shoulder while working, as this can lead to neck strain.
Messages: Don’t use the computer while conveying messages in person or through the intercom.
No games:One of the main Causes of Repetitive Stress Injury is Games. Games or surfing at work may increase stress on your hands. So games should be avoided.
Preventive Measures at the Organizational Level for Repetitive Stress injury : –
Organizations that use computers in a big way can also adopt certain preventive measures for avoiding Repetitive Strain Injury to their employees. These include:
1.You need to educate your employees on the importance of adopting a proper posture which is one of the main cause of Repetitive Stress Injury.
2.Ensure that all your employees are using quality ergonomic furniture that will save loss of working hours by guaranteeing full comfort of the employees.
3.Give periodic reminders through lectures and audio-visual presentations by medical professionals on the importance of taking good care of health while using computers and Repetitive Stress Injury.
4.Try to avoid computer as much as possible: use voicemail instead of sending e-mail. Go for a walk or watch a movie instead of playing video games. Its better go for a book instead of searching the Web. You are in the danger zone for Repetitve Stress Injury if you are using a computer for as little as two hours a day.
5.Adjust your workstation properly. Make sure your monitor is directly in front of you, with the top of the screen at eye level. Be sure your keyboard (Ergonomic Keyboard) and mouse (Ergonomic Mouse) are low enough to allow you to relax your shoulders.
6.Sit up straight. Make sure your chair supports your spine in an erect position as it is the one of the main causes of Repetitive Stress Injury.
7.Practice proper technique: never rest your wrists on the desk, wrist pad or armrests while you are typing or using a mouse or trackball.
8.Pace yourself. Take a 5-to-10 minute break every 20 minutes and limit your overall time at the computer.
9.Get regular cardiovascular exercise.
10.Do appropriate upper-body strengthening and stretching exercises.
11.Stretch frequently while at the computer.
12.Do not work at the computer or other hand-intensive activities if you are experiencing pain, fatigue or soreness.
13.Avoid using the mouse and trackball whenever possible. Use keystrokes instead for preventing Repetitive Stress Injury.
14.When symptoms of Repetitive Stress Injury are set in, consult an orthopedic surgeon. If you find of the symptoms of Repetitive Stress Injury mentioned above, do not make the diagnosis yourself. The diagnosis will be made from the history and clinical findings as there will be no changes in X-rays, since the soft tissues are involved.
Nerve conduction studies can confirm the diagnosis. In cases detected earlier, attention to ergonomics will restore normalcy.
In cases of Repetitive Stress Injury when diagnosed late, orthopedic treatment like injections and even minor surgery may be necessary.
You may click to see this page for more knowledge
Disclaimer: This information is not meant to be a substitute for professional medical advise or help. It is always best to consult with a Physician about serious health concerns. This information is in no way intended to diagnose or prescribe remedies.This is purely for educational purpose.
Related articles
- Is Your iPad Causing Your Chronic Pain? (everydayhealth.com)
- Repetitive Strain Injuries: Three Easy Ways to Reduce the Risk of Operator Related Trauma (prweb.com)
- Why is the tip of my finger numb? (zocdoc.com)
- Tablet and Smart Phone Use Becoming Number One Cause of Joint and Muscle Pain in North America (prweb.com)
- Charlene Tessier: Reverse Your RSI (frenchfortunecookie.wordpress.com)
- What Are Treatments for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome – Dr. J. Michael Bennett (orthopedicsportsdoctor.com)
- What Are Treatments for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome – Orthopedic Doctor Houston TX (orthopedicsportsdoctor.com)
- Kids are hi-tech wrecks with adult injuries (heraldsun.com.au)
- Penclic Wireless Mouse (PWM) (niranjblog.wordpress.com)
- Wench Ergonomics (wordwenches.typepad.com)
Resources:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Repetitive_strain_injury
http://www.safecomputingtips.com/rsi-diagnosis.html
http://www.bbc.co.uk/health/physical_health/conditions/repetitivestrain1.shtml
http://www.rsiwarrior.com/ergonomics.html
http://www.hoverstop.com/eng/rsi.php
Related articles
- Repetitive strain injury(RSI) (findmeacure.com)
- Is Your iPad Causing Your Chronic Pain? (everydayhealth.com)
- Repetitive Strain Injuries: Three Easy Ways to Reduce the Risk of Operator Related Trauma (prweb.com)
- Health Tip: Warning Signs of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (nlm.nih.gov)
- Massage Therapy Benefits Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Hand Pain? (massageenvy.com)
- Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Treatment – Orthopedic Surgeon – Richmond TX (orthopedicsportsdoctor.com)
- Computer borne illness (dmohankumar.wordpress.com)
- Texting Can Be a Real Pain in the Neck (blogs.vancouversun.com)
- Ergonomic Wireless Mouse Reduces Repetitive Strain on Your Neck and Shoulders (smarthome.com)


![Reblog this post [with Zemanta]](https://i0.wp.com/img.zemanta.com/reblog_e.png?w=580)









