[amazon_link asins=’B01LFE53LU,B00YI2S0P8′ template=’ProductCarousel’ store=’finmeacur-20′ marketplace=’US’ link_id=’e66dd81c-ee88-11e6-8bf6-a3594564779f’]
[amazon_link asins=’B001W2QE9G,B01N2BI02K,B01EARHZYW,B01J7Z4GRG,B01L2B1URM,B0058AASOA,B01DPSBE12,B01M243O6B’ template=’ProductCarousel’ store=’finmeacur-20′ marketplace=’US’ link_id=’f43d64a1-0c5f-11e7-af57-2105d908785a’]
Alternative Names:
Fungal infection – groin; Infection – fungal – groin; Itching in the groin; Ringworm – groin; Tinea cruris; Tinea of the groin.
Definition:
Jock itch is an infection of the groin area caused by fungus. It is a fungal infection affecting the moist skin on inner thighs, genitals, anal area, or buttocks, appearing in both men and women. Affected skin is covered by red or brown rash that may be ring-shaped. Rash may itch or burn; affected skin may peel off or crack.
You may click to see the pictures
click to see the pictures>.....(1).……..(2).....….
Causes:
The body normally hosts a variety of bacteria and fungi. Some of these are useful to the body. Others can multiply rapidly and form infections. Jock itch occurs when a particular type of fungus grows and multiplies in the groin area.
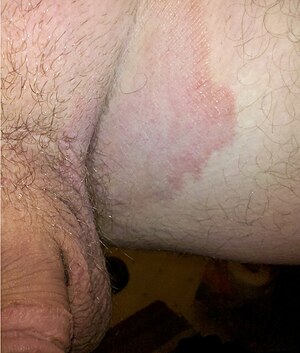
Jock itch occurs mostly in adult men and adolescent boys. It can sometimes accompany athlete’s foot and ringworm. The fungus that causes jock itch thrives in warm, moist areas. Jock itch can be triggered by friction from clothes and prolonged wetness in the groin area (such as from sweating).
Jock itch may be contagious. It can be passed from one person to the next by direct skin-to-skin contact or contact with unwashed clothing. Jock itch usually stays around the creases in the upper thigh and does not involve the scrotum or penis. It is often less severe than other tinea infections, but may last a long time. Jock itch may spread to the anus, causing anal itching and discomfort.
Other causes of itching in the groin include:-
*Lichen simplex chronicus
*Eczema
*Pubic lice
*Chemical irritation
You may click & See also: Vaginal itching
.
How Jock Itch Spreads?
Jock itch is easily spread with sharing towels or sportswear, or with sexual contact.
Who Normly Gets Infected?
Adult men that often have moist groin are often infected. Jock itch may also appear in women. It rarely appears before 15 years of age.
Risk factors for getting jock itch are:–
*Wet groin; (male athletes, dhobi itch is known in western washermen)
*Tight underwear
*Obesity; infection occurs in wet skin folds
*Immunodeficiency: AIDS, diabetes
Possible Completications:–
Complications are infrequent since jock itch is usually a self-limited skin condition. Rarely, the rash may spread past the groin onto the thighs and genitals. Secondary skin infections from scratching or rubbing can uncommonly deepen, causing cellulitis or abscess formation.
Another potential complication includes temporary skin discoloration called post-inflammatory hypopigmentation (lighter than the regular skin color) or hyperpigmentation (darker then the regular skin color). This altered skin color may occur after the rash has improved or after a temporary flare. Permanent scarring is uncommon.
.Symptoms:
Jock itch usually begins with mild intermittent itching in the groin. The itching can get worse and become unbearable in some cases. The rash is usually on both sides of the groin and affects the folds.
The rash may become dry, rough, and bumpy, develop pus bumps, or begin to ooze. Sometimes, the uppermost skin clears as the rash spreads further down onto the thighs. The itching and rash can spread to the genitals including the labia, vagina, scrotum, penis, and anus.
Women may also develop vaginal white discharge and yeast infections. Men may develop infections on the head of the penis, especially if they are not circumcised.
Severe cases may be very uncomfortable and develop secondary complications such as breaks in the skin, open sores, ulcers, and rarely cellulitis.
.Diagnosis:
Doctor will usually diagnose jock itch based on the appearance of the skin. Tests are usually not necessary. If tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis, either a culture or a skin lesion biopsy (for example, a scraping of the skin) may show the fungus that causes jock itch.
Rash in the groin may be caused by other types of fungi (Candida albicans), viruses (Herpes genitalis), bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus), allergies (itchy pants syndrome, cholinergic urticaria), inverted psoriasis, Darier’s disease, Hailey-Hailey disease (pemphigus), intertrigo, seborrheic dermatitis, etc.
Treatment:-
There are many treatment options and skin-care recipes for treating jock itch. Since the two primary causes of jock itch are excess moisture and fungal infections, treatment depends on the exact cause of the jock itch. Treatment of jock itch associated with skin irritation and excess moisture should address general measures to keep the groin clean and dry. Treatment of fungal jock itch should include antifungal creams used continuously for two to four weeks.
It is important to keep in mind that no therapy is uniformly effective in all people. Doctor may need to help evaluate the cause of your jock itch.
Home Remedy:-
Home remedy for mild jock itch includes:
*washing the groin skin two to three times a day with a gentle soapless cleanser like Dove non-soap cleanser or Cetaphil and water;
*keeping the groin area dry;
*avoiding excess groin skin irritation by wearing 100% cotton underwear;
*avoiding fabric softeners, bleaches, or harsh laundry detergents; and
*applying a mix of over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream and clotrimazole (Lotrimin, Mycelex) cream one to two times a day to the affected area.
Holistic jock itch treatments:-
Holistic (nonmedicated) home remedy options for jock itch include:
*Soaking the affected area daily with a washcloth dipped in dilute white vinegar (1 part vinegar to 4 parts of water) and drying the skin and
*Soaking in a bathtub daily or every other day with very dilute Clorox bleach (1 quarter cup of Clorox bleach in a bathtub full of water) and drying the skin.
Fungal jock itch is treated Normally as follows:-
Mild fungal or yeast jock itch may be treated by:
*Washing groin twice daily with an antifungal shampoo like ketoconazole (Nizoral shampoo) or seleni
um sulfide (Selsun Blue shampoo).
Moderate fungal or yeast jock itch is often treated by a combination of:
*washing the groin twice daily with an antifungal shampoo like ketoconazole or selenium sulfide and
*Using a topical antifungal cream like miconazole (Monistat, Micatin), clotrimazole or terbinafine (Lamisil).
Severe fungal or yeast jock itch is typically treated by a combination of:
*Washing groin twice daily with an antifungal shampoo like ketoconazole or selenium sulfide,
*Using a topical antifungal cream like miconazole, clotrimazole or terbinafine, and
*Taking an antifungal pill like fluconazole (Diflucan), itraconazole (Sporanox), or terbinafine.
Bacterial jock itch is normally treated as follows:-
Mild bacterial jock itch may be treated with:
*Antibacterial skin washes like Lever 2000 soap or chlorhexidine (Hibiclens) soap twice daily.
Moderate bacterial jock itch may be treated with:
*Antibacterial skin washes like chlorhexidine soap twice daily and
*Twice-daily application of a topical antibiotic like clindamycin lotion or metronidazole (Flagyl) lotion.
Severe bacterial jock itch may be treated with:–
*Antibacterial skin washes like chlorhexidine soap twice daily,
*Twice-daily application of a topical antibiotic like clindamycin lotion or metronidazole lotion, and
*A five- to 14-day course of an oral antibiotic like cephalexin (Keflex), dicloxacillin, doxycyline, minocycline (Dynacin, Minocin), tetracycline (Sumycin), ciprofloxacin (Cipro, Cipro XR, Proquin XR), or levofloxacin (Levaquin) for more resistant situations.
Treatment of Inflammatory itching :-
Inflammatory itching from jock itch can be treated with a short course of one of the following:
*Use a short five- to seven-day course of a mild to medium potency, topical steroid cream like prescription triamcinolone 0.025% once or twice a day for inflamed or itchy areas.
*Use a short five- to seven-day course of a mild over-the-counter topical steroid cream like hydrocortisone (Cortaid) one to three times a day for itching.
*Use a topical immunomodulator such as pimecrolimus (Elidel) cream or tacrolimus (Protopic) ointment twice a day. Although these creams are approved for atopic dermatitis and eczema, their use would be considered “off label” (non-FDA labeled use) for jock itch.
Causes of Residual skin discoloration :–
Residual skin discoloration in the groin may persist for weeks to months after more severe forms of jock itch clear. This darkish discoloration is called hyperpigmentation and may be treated with one or a combination of
*Hydroquinone 4% cream,
*Kojic acid cream,
*Azelaic acid 15% cream,
*Over-the-counter fading cream with 2% hydroquinone (Porcelana), or
*Specially designed prescription creams for particularly resistant skin discoloration using higher concentrations of hydroquinone 6%, 8%, and 10% may also be formulated by prescription by compounding pharmacists.
Best Drug for Jock Itch:-
Overall, the best jock-itch drug is a topical antifungal cream like miconazole, clotrimazole, or terbinafine. If the jock itch does not improve within two to three weeks of treatment, then a physician should be consulted.
You may click to see Herbal Treatment of Jock Itch...(1)…...(2):…..(3):
Homeopathic Treatment.……….(1)
Prognosis:-
The prognosis with jock itch is very good. Overall, jock itch tends to be an easily treated and curable skin condition. Commonly, it is a mild, benign, usually noncontagious, and self-limited skin condition. More widespread, atypical cases of jock itch may be embarrassing, chronically disfiguring, and psychologically distressing for the patient.
Prevention:
Jock itch prevention efforts include good general skin hygiene and keeping your groin clean and dry. The following preventive steps will help:
*Wash groin and buttocks with soap and water after exercise and sweating.
*Wash workout clothes, underwear, and swimwear after each use.
*Minimize groin moisture by using white cotton underwear.
*Change underwear frequently and especially after sweating.
*Wash clothes and undergarments in hot soapy water.
*Use loose-fitting cotton underwear and clothing.
*Avoid undergarments with polyesters, nylon, or synthetic fibers.
*Use an antifungal powder like Lamisil or Zeasorb to keep the groin dry.
*Avoid fragranced or irritating creams or lotions on the groin.
*Avoid going barefoot, especially at gyms, schools, and public pools.
*Treat athlete’s foot if you have it.
*Cover your feet with socks before you put on your underwear and pants.
Disclaimer: This information is not meant to be a substitute for professional medical advise or help. It is always best to consult with a Physician about serious health concerns. This information is in no way intended to diagnose or prescribe remedies.This is purely for educational purpose.
Resources:
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000876.htm
http://www.medicinenet.com/jock_itch/page3.htm
Related articles by Zemanta
- Armpit Fungus – Sweat, Irritation & Perfume Allergy (healthhype.com)
- Ringworm Fungal Infections – Skin Fungus (healthhype.com)
- The four grossest kid health problems (cnn.com)
- Beateczema – How To Stop Eczema (slideshare.net)
- Beateczema – Herbal Remedies For Eczema (slideshare.net)
- Mounting a multi-layered attack on fungal infections (scienceblog.com)
- Itchy Bottom (healthhype.com)



