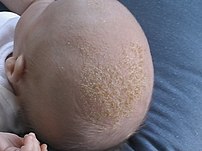
Introduction:
The loss of skin cells from the scalp is a normal part of the life cycle of skin cells.Every day we lose dead skin cells from our scalps. When more are lost than normal, they clump together forming the white or grey flakes called dandruff. However, excessive flaking of the scalp, or dandruff, is a common cosmetic problem experienced by millions of people. Dandruff is not contagious and is normally not a serious problem. Some cases of excessive dandruff accompanied by intense itching and patches of flaky skin on the face or elsewhere are actually a form of eczema referred to as seborrheic eczema.

Dandruff can form when the scalp is too dry or too oily. A fungus called pityrosporum ovale, which lives naturally on the scalp, has been implicated in the development of dandruff. Excess production of sebum, the natural oil secreted from glands in the skin, fuels the growth of this fungus. This helps to explain why dandruff often starts in puberty when hormone changes occur and why people with oily scalps suffer more.
Dandruff is believed to run in families. Diets that are too salty, spicy or sugary and accompanied by too much alcohol make it worse, as can stress and changes in climate.
Nutritional deficiencies, such as a lack of essential fatty acids or vitamin B, may cause dandruff.
Seborrhoeic eczema causes itchy and flaky patches on the scalp. This tends to be more severe than simple dandruff because the skin and glands become inflamed. The flakes are often greasier and more yellow in colour and can also affect the eyebrows, ears, face and upper body.
.
Symptoms:
People with flaky, itchy scalp will notice dead skin cells on the scalp that look like white or gray flakes. Some people may misdiagnosis the flakes as dandruff, but they tend to be larger than regular dandruff flakes.
Red Scalp..…..
With flaky, itchy scalp, the scalp can become red and irritated. Pain may or may not be associated with a swollen, red scalp.
Itchy Scalp….
As indicated in the name, flaky, itchy scalp is accompanied by an itchy feeling. Avoid scratching, as this can worsen the condition.
TScalp..ense ….
The scalp can become tight and tense. You may experience the feeling that all the blood is rushing to your head.
Dull Hair…
With flaky, itchy scalp, the hair becomes dull and lifeless. This is due to a lack of moisture reaching the scalp.
Treatment:
Anti-dandruff shampoos are the mainstay of treatment for simple dandruff. It’s usually trial and error finding the one that works for you.
For more stubborn dandruff or seborrhoeic eczema, selenium, zinc, coal tar in coconut oil or salicylic acid can be successful. Scalp preparations contain various combinations of these. Be careful when using tar, however, as it can discolour fair hair and bed linen.
Antifungal shampoos containing ketoconazole work well for dandruff and seborrhoeic eczema. They need to be used a few times a week. Be patient: they can take up to six weeks to work.
All these treatments are available from the pharmacist without a prescription.
You may click to see :
*Simple Home Remedy for Flaky scalp….
*Ayurvrdic Treatment of Flaky Scalp
When to go to Doctor?
If your scalp isn’t getting better with these treatments, or if it’s red, inflamed or painful, a different treatment may be needed.
Steroid lotion or mousse is used for severe seborrhoeic eczema. It’s also used to treat psoriasis, which not only affects the elbows and knees, but also the scalp.
Psoriasis occurs when new skin cells are made too quickly. The build up of these cells creates red areas covered with thick, scaly, silvery-looking patches, which can be very uncomfortable and itchy.
Prevention:
When shampooing, massage your scalp and don’t scratch it. Rinse your hair well, ideally twice with every shampoo. The scalp is very sensitive, so take care with hair products that can dry and irritate it.
Alternate your usual shampoo with a dandruff shampoo. If you find the flakes make an unwelcome return, don’t panic. This often happens, just switch to a new shampoo.
Make sure your diet contains enough vitamins E, B6 and B12, selenium and zinc. Flaxseed oil is also said to help prevent dandruff and can be taken in liquid or capsule form.
It’s a myth that dandruff is:
•Infectious
•Makes you go bald sooner
•Only affects dark-haired people
•Means you don’t wash your hair enough
Disclaimer: This information is not meant to be a substitute for professional medical advise or help. It is always best to consult with a Physician about serious health concerns. This information is in no way intended to diagnose or prescribe remedies.This is purely for educational purpose.
Resources:
http://www.bbc.co.uk/health/physical_health/conditions/flakyscalp1.shtml
http://www.wrongdiagnosis.com/sym/flaky_scalp.htm
http://www.themedicalplus.com/2010/01/28/scalp-health-zincplex/
http://www.ehow.com/facts_5007089_symptoms-flaky-itchy-scalp.html
Related articles
- Dry Scalp and Dandruff: What’s Causing Those Flakes? (everydayhealth.com)
- Getting to the Root of Scalp Eczema (everydayhealth.com)
- What’s Causing Flaky Patches on the Scalp? (everydayhealth.com)
- 7 Dry Scalp Treatments (everydayhealth.com)
- Best Remedies for Severe Dandruff (healthadel.com)
- Cradle Cap (findmeacure.com)