[amazon_link asins=’B01N3SF42Q,1936251019,B008ACAKNC,0198738269,B016XMVHGO,1587792494,B01I38YKKQ,0061417262′ template=’ProductCarousel’ store=’finmeacur-20′ marketplace=’US’ link_id=’0ebecf5f-086e-11e7-b63d-6fdd90315765′][amazon_link asins=’0198738269,3319305506,3662510456,1405138890,1605949647,1434810607,B01GCEY1M0,3330041021′ template=’ProductCarousel’ store=’finmeacur-20′ marketplace=’US’ link_id=’ca6cba20-086d-11e7-a188-6752871b9377′][amazon_link asins=’542102136X,B013XE6F8U,B00ZPMGCLO,B00RBPI8EC,B01FKEX980,0006046460,B01MR4RJJB,B00M28FJZO,B00XQF6PEQ’ template=’ProductCarousel’ store=’finmeacur-20′ marketplace=’US’ link_id=’a79a8b6f-086d-11e7-9895-8549e8541338′]
“Baby bottle caries”,Dental caries is an infectious disease which damages the structures of teeth. Tooth decay or cavities are consequences of caries. If left untreated, the disease can lead to pain, tooth loss, infection, and, in severe cases, death of the tooth.
CLICK TO SEE…>…...(01)...(1).…….(2).…....(3)..…...(4).
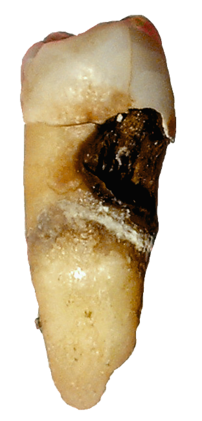
.Destruction of a tooth by cervical decay from dental caries
There is a long history of dental caries, with evidence showing the disease was present in the Bronze, Iron, and Medieval ages but also prior to the neolithic period. The largest increases in the prevalence of caries have been associated with diet changes. Today, it remains one of the most common diseases throughout the world.
There are numerous ways to classify dental caries. Although the presentation may differ, the risk factors and development among distinct types of caries remain largely similar. Initially, it may appear as a small chalky area but eventually develop into a large, brown cavitation. Though sometimes caries may be seen directly, radiographs are frequently needed to inspect less visible areas of teeth and to judge the extent of destruction.
Tooth decay is caused by certain types of acid-producing bacteria which cause damage in the presence of fermentable carbohydrates such as sucrose, fructose, and glucose. The resulting acidic levels in the mouth affect teeth because a tooth’s special mineral content causes it to be sensitive to low pH. Specifically, a tooth (which is primarily mineral in content) is in a constant state of back-and-forth demineralization and remineralization between the tooth and surrounding saliva. When the pH at the surface of the tooth drops below 5.5, demineralization proceeds faster than remineralization (i.e. there is a net loss of mineral structure on the tooth’s surface). This results in the ensuing decay. Depending on the extent of tooth destruction, various treatments can be used to restore teeth to proper form, function, and aesthetics, but there is no known method to regenerate large amounts of tooth structure. Instead, dental health organizations advocate preventive and prophylactic measures, such as regular oral hygiene and dietary modifications, to avoid dental caries.
Epidemiology:
An estimated 90% of schoolchildren worldwide and most adults have experienced caries, with the disease being most prevalent in Asian and Latin American countries and least prevalent in African countries. In the United States, dental caries is the most common chronic childhood disease, being at least five times more common than asthma. It is the primary pathological cause of tooth loss in children. Between 29% and 59% of adults over the age of fifty experience caries.
The number of cases has decreased in some developed countries, and this decline is usually attributed to increasingly better oral hygiene practices and preventive measures such as fluoride treatment. Nonetheless, countries that have experienced an overall decrease in cases of tooth decay continue to have a disparity in the distribution of the disease. Among children in the United States and Europe, 60-80% of cases of dental caries occur in 20% of the population. A similarly skewed distribution of the disease is found throughout the world with some children having none or very few caries and others having a high number. Some countries, such as Australia, Nepal, and Sweden, have a low incidence of cases of dental caries among children, whereas cases are more numerous in Costa Rica and Slovakia.
Clasification:
Caries can be classified by location, etiology, rate of progression, and affected hard tissues. When used to characterize a particular case of tooth decay, these descriptions more accurately represent the condition to others and may also indicate the severity of tooth destruction.
Location:
Generally, there are two types of caries when separated by location: caries found on smooth surfaces and caries found in pits and fissures. The location, development, and progression of smooth-surface caries differ from those of pit and fissure caries.
Pit and fissure caries:
Pits and fissures are anatomic landmarks on a tooth where tooth enamel infolds creating such an appearance. Fissures are formed during the development of grooves, and have not fully fused (unlike grooves), thus possessing a unique linear-like small depression in enamel’s surface structure, which would be a great place for dental caries to develop and flourish.
CLICK TO SEE
The pits and fissures of teeth provide a location for caries formation
Fissures are mostly located on the occlusal (chewing) surfaces of posterior teeth and palatal surfaces of maxillary anterior teeth. Pits are small, pinpoint depressions that are found at the ends or cross-sections of grooves. In particular, buccal pits are found on the facial surface of molars. For all types of pits and fissures, the deep infolding of enamel makes oral hygiene along these surfaces difficult, allowing dental caries to be common in these areas.
The occlusal surfaces of teeth represent 12.5% of all tooth surfaces but are the location of over 50% of all dental caries.
Among children, pit and fissure caries represent 90% of all dental caries. Pit and fissure caries can sometimes be difficult to detect. As the decay progresses, caries in enamel nearest the surface of the tooth spreads gradually deeper. Once the caries reaches the dentin at the dentino-enamel junction, the decay quickly spreads laterally. Within the dentin, the decay follows a triangle pattern that points to the tooth’s pulp. This pattern of decay is typically described as two triangles (one triangle in enamel, and another in dentin) with their bases conjoined to each other at the dentino-enamel junction (DEJ). This base-to-base pattern is typical of pit and fissure caries, unlike smooth-surface caries (where base and apex of the two triangles join).
Smooth-surface caries
There are three types of smooth-surface caries. Proximal caries, also called interproximal caries, form on the smooth surfaces between adjacent teeth. Root caries form on the root surfaces of teeth. The third type of smooth-surface caries occur on any other smooth tooth surface.
CLICK & SEE
In this radiograph, the dark spots in the adjacent teeth show proximal caries
Proximal caries are the most difficult type to detect. Frequently, this type of caries cannot be detected visually or manually with a dental explorer. Proximal caries form cervically (toward the roots of a tooth) just under the contact between two teeth. As a result, radiographs are needed for early discovery of proximal caries.
Root caries, which are sometimes described as a category of smooth-surfaces caries, are the third most common type of caries and usually occur when the root surfaces have been exposed due to gingival recession. When the gingiva is healthy, root caries is unlikely to develop because the root surfaces are not as accessible to bacterial plaque. The root surface is more vulnerable to the demineralization process than enamel because cementum begins to demineralize at 6.7 pH, which is higher than enamel’s critical pH. Regardless, it is easier to arrest the progression of root caries than enamel caries because roots have a greater reuptake of fluoride than enamel. Root caries are most likely to be found on facial surfaces, then interproximal surfaces, then lingual surfaces. Mandibular molars are the most common location to find root caries, followed by mandibular premolars, maxillary anteriors, maxillary posteriors, and mandibular anteriors.
Lesions on other smooth surfaces of teeth are also possible. Since these occur in all smooth surface areas of enamel except for interproximal areas, these types of caries are easily detected and are associated with high levels of plaque and diets promoting caries formation.
Other general descriptions:
Besides the two previously mentioned categories, carious lesions can be described further by their location on a particular surface of a tooth. Caries on a tooth’s surface that are nearest the cheeks or lips are called “facial caries”, and caries on surfaces facing the tongue are known as “lingual caries”. Facial caries can be subdivided into buccal (when found on the surfaces of posterior teeth nearest the cheeks) and labial (when found on the surfaces of anterior teeth nearest the lips).
Lingual caries can also be described as palatal when found on the lingual surfaces of maxillary teeth because they are located beside the hard palate.Caries near a tooth’s cervix—the location where the crown of a tooth and its roots meet—are referred to as cervical caries.
Occlusal caries are found on the chewing surfaces of posterior teeth. Incisal caries are caries found on the chewing surfaces of anterior teeth. Caries can also be described as “mesial” or “distal.” Mesial signifies a location on a tooth closer to the median line of the face, which is located on a vertical axis between the eyes, down the nose, and between the contact of the central incisors. Locations on a tooth further away from the median line are described as distal.
Etiology:
In some instances, caries are described in other ways that might indicate the cause. “Baby bottle caries”, “early childhood caries”, or “baby bottle tooth decay” is a pattern of decay found in young children with their deciduous (baby) teeth. The teeth most likely affected are the maxillary anterior teeth, but all teeth can be affected. The name for this type of caries comes from the fact that the decay usually is a result of allowing children to fall asleep with sweetened liquids in their bottles or feeding children sweetened liquids multiple times during the day.
.CLICK TO SEE
………….Rampant caries as seen here may be due to methamphetamine use.
Another pattern of decay is “rampant caries”, which signifies advanced or severe decay on multiple surfaces of many teeth. Rampant caries may be seen in individuals with xerostomia, poor oral hygiene, methamphetamine use (due to drug-induced dry mouth, and/or large sugar intake. If rampant caries is a result from previous radiation to the head and neck, it may be described as radiation-induced caries. Problems can also be caused by the self destruction of roots and whole Tooth Resorption when new teeth erupt or later from unknown causes.
Rate of progression:
Temporal descriptions can be applied to caries to indicate the progression rate and previous history. “Acute” signifies a quickly developing condition, whereas “chronic” describes a condition which has taken an extended time to develop. Recurrent caries, also described as secondary, is caries that appears at a location with a previous history of caries. This is frequently found on the margins of fillings and other dental restorations. On the other hand, incipient caries describes decay at a location that has not experienced previous decay. Arrested caries describes a lesion on a tooth which was previously demineralized but was remineralized before causing a cavitation.
Affected hard tissue:
Depending on which hard tissues are affected, it is possible to describe caries as involving enamel, dentin, or cementum.
Early in its development, caries may affect only enamel. Once the extent of decay reaches the deeper layer of dentin, “dentinal caries” is used. Since cementum is the hard tissue that covers the roots of teeth, it is not often affected by decay unless the roots of teeth are exposed to the mouth. Although the term “cementum caries” may be used to describe the decay on roots of teeth, very rarely does caries affect the cementum alone. Roots have a very thin layer of cementum over a large layer of dentin, and thus most caries affecting cementum also affects dentin.
Signs and symptoms:
Until caries progresses, a person may not be aware of it. The earliest sign of a new carious lesion, referred as incipient decay, is the appearance of a chalky white spot on the surface of the tooth, indicating an area of demineralization of enamel. As the lesion continues to demineralize, it can turn brown but will eventually turn into a cavitation, a “cavity”.
The process before this point is reversible, but once a cavitation forms, the lost tooth structure cannot be regenerated. A lesion which appears brown and shiny suggests dental caries was once present but the demineralization process has stopped, leaving a stain. A brown spot which is dull in appearance is probably a sign of active caries.
As the enamel and dentin are destroyed further, the cavitation becomes more noticeable. The affected areas of the tooth change color and become soft to the touch. Once the decay passes through enamel, the dentinal tubules, which have passages to the nerve of the tooth, become exposed and cause the tooth to hurt. The pain can be worsened by heat, cold, or sweet foods and drinks. Dental caries can also cause bad breath and foul tastes. In highly progressed cases, infection can spread from the tooth to the surrounding soft tissues which may become life-threatening, as in the case with Ludwig’s angina.
Diagnosis:
Primary diagnosis involves inspection of all visible tooth surfaces using a good light source, dental mirror and explorer.
CLICK & SEE.
Dental radiographs, produced when X-rays are passed through the jaw and picked up on film or digital sensor, may show dental caries before it is otherwise visible, particularly in the case of caries on interproximal (between the teeth) surfaces.
Large dental caries are often apparent to the naked eye, but smaller lesions can be difficult to identify. Unextensive dental caries was formerly found by searching for soft areas of tooth structure with a dental explorer. Visual and tactile inspection along with radiographs are still employed frequently among dentists, particularly for pit and fissure caries.
Some dental researchers have cautioned against the use of dental explorers to find caries. In cases where a small area of tooth has begun demineralizing but has not yet cavitated, the pressure from the dental explorer could cause a cavitation.
Since the carious process is reversible before a cavitation is present, it may be possible to arrest the caries with fluoride to remineralize the tooth surface. When a cavitation is present, a restoration will be needed to replace the lost tooth structure. A common technique used for the diagnosis of early (uncavitated) caries is the use of air blown across the suspect surface, which removes moisture, changing the optical properties of the unmineralized enamel. This produces a white ‘halo’ effect detectable to the naked eye. Fiberoptic transillumination, lasers and disclosing dyes have been recommended for use as an adjunct when diagnosing smaller carious lesions in pits and fissures of teeth.
Causes:
There are four main criteria required for caries formation: a tooth surface (enamel or dentin); cariogenic (or potentially caries-causing) bacteria; fermentable carbohydrates (such as sucrose); and time. The caries process does not have an inevitable outcome, and different individuals will be susceptible to different degrees depending on the shape of their teeth, oral hygiene habits, and the buffering capacity of their saliva. Dental caries can occur on any surface of a tooth that is exposed to the oral cavity, but not the structures which are retained within the bone.
Teeth:
There are certain diseases and disorders affecting teeth which may leave an individual at a greater risk for caries.
Amelogenesis imperfecta, which occurs between 1 in 718 and 1 in 14,000 individuals, is a disease in which the enamel does not form fully or in insufficient amounts and can fall off a tooth.Dentinogenesis imperfecta is a similar disease. In both cases, teeth may be left more vulnerable to decay because the enamel is not as able to protect the tooth as it would in health.
In most people, disorders or diseases affecting teeth are not the primary cause of dental caries. Ninety-six percent of tooth enamel is composed of minerals. These minerals, especially hydroxyapatite, will become soluble when exposed to acidic environments. Enamel begins to demineralize at a pH of 5.5. Dentin and cementum are more susceptible to caries than enamel because they have lower mineral content. Thus, when root surfaces of teeth are exposed from gingival recession or periodontal disease, caries can develop more readily. Even in a healthy oral environment, the tooth is susceptible to dental caries.
The anatomy of teeth may affect the likelihood of caries formation. In cases where the deep grooves of teeth are more numerous and exaggerated, pit and fissure caries are more likely to develop. Also, caries are more likely to develop when food is trapped between teeth.
Bacteria:
The mouth contains a wide variety of bacteria, but only a few specific species of bacteria are believed to cause dental caries: Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacilli among them. Particularly for root caries, the most closely associated bacteria frequently identified are Lactobacillus acidophilus, Actinomyces viscosus, Nocardia spp., and Streptococcus Bacteria collect around the teeth and gums in a sticky, creamy-coloured mass called plaque, which serves as a biofilm. Some sites collect plaque more commonly than others. mutans.
.A gram stain image of Streptococcus mutans.
The grooves on the biting surfaces of molar and premolar teeth provide microscopic retention, as does the point of contact between teeth. Plaque may also collect along the gingiva. In addition, the edges of fillings or crowns can provide protection for bacteria, as can intraoral appliances such as orthodontic braces or removable partial dentures.
Fermentable carbohydrates:
Bacteria in a person’s mouth convert sugars (glucose and fructose, and most commonly sucrose – or table sugar) into acids such as lactic acid through a glycolytic process called fermentation. If left in contact with the tooth, these acids may cause demineralization, which is the dissolution of its mineral content. The process is dynamic, however, as remineralization can also occur if the acid is neutralized; suitable minerals are available in the mouth from saliva and also from preventative aids such as fluoride toothpaste, dental varnish or mouthwash. Caries advance may be arrested at this stage. If sufficient acid is produced over a period of time to the favor of demineralization, caries will progress and may then result in so much mineral content being lost that the soft organic material left behind would disintegrate, forming a cavity or hole.
Time:
The frequency of which teeth are exposed to cariogenic (acidic) environments affects the likelihood of caries development. After meals or snacks containing sugars, the bacteria in the mouth metabolize them resulting in acids as by-products which decreases pH. As time progresses, the pH returns to normal due to the buffering capacity of saliva and the dissolved mineral content from tooth surfaces. During every exposure to the acidic environment, portions of the inorganic mineral content at the surface of teeth dissolves and can remain dissolved for 2 hours. Since teeth are vulnerable during these periods of acidic environments, the development of dental caries relies greatly on the frequency of these occurrences.
For example, when sugars are eaten continuously throughout the day, the tooth is more vulnerable to caries for a longer period of time, and caries are more likely to develop than if teeth are exposed less frequently to these environments and proper oral hygiene is maintained. This is because the pH never returns to normal levels, thus the tooth surfaces cannot remineralize, or regain lost mineral content.
The carious process can begin within days of a tooth erupting into the mouth if the diet is sufficiently rich in suitable carbohydrates, but may begin at any other time thereafter. The speed of the process is dependent on the interplay of the various factors described above but is believed to be slower since the introduction of fluoride. Compared to coronal smooth surface caries, proximal caries progress quicker and take an average of 4 years to pass through enamel in permanent teeth. Because the cementum enveloping the root surface is not nearly as durable as the enamel encasing the crown, root caries tends to progress much more rapidly than decay on other surfaces. The progression and loss of mineralization on the root surface is 2.5 times faster than caries in enamel. In very severe cases where oral hygiene is very poor and where the diet is very rich in fermentable carbohydrates, caries may cause cavitation within months of tooth eruption. This can occur, for example, when children continuously drink sugary drinks from baby bottles. On the other hand, it may take years before the process results in a cavity being formed, if at all.
Other risk factors:
In addition to the four main requirements for caries formation, reduced saliva is also associated with increased caries rate since the buffering capability of saliva is not present to counterbalance the acidic environment created by certain foods. As a result, medical conditions that reduce the amount of saliva produced by salivary glands, particularly the parotid gland, are likely to cause widespread tooth decay. Some examples include Sjögren’s syndrome, diabetes mellitus, diabetes insipidus, and sarcoidosis. Medications, such as antihistamines and antidepressants, can also impair salivary flow. Moreover, 63% of the most commonly prescribed medications in the United States list dry mouth as a known side effect. Radiation therapy to the head and neck may also damage the cells in salivary glands, increasing the likelihood for caries formation.
The use of tobacco may also increase the risk for caries formation. Smokeless tobacco frequently contains high sugar content in some brands, possibly increasing the susceptibility to caries. Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for periodontal disease, which can allow the gingiva to recede. As the gingiva loses attachment to the teeth, the root surface becomes more visible in the mouth. If this occurs, root caries is a concern since the cementum covering the roots of teeth is more easily demineralized by acids in comparison to enamel. Currently, there is not enough evidence to support a causal relationship between smoking and coronal caries, but there is suggestive evidence of a causal relationship between smoking and root-surface caries
Treatment:
Destroyed tooth structure does not fully regenerate, although remineralization of very small carious lesions may occur if dental hygiene is kept at optimal level. For the small lesions, topical fluoride is sometimes used to encourage remineralization. For larger lesions, the progression of dental caries can be stopped by treatment. The goal of treatment is to preserve tooth structures and prevent further destruction of the tooth.
Generally, early treatment is less painful and less expensive than treatment of extensive decay. Anesthetics local, nitrous oxide (“laughing gas”), or other prescription medications — may be required in some cases to relieve pain during or following treatment or to relieve anxiety during treatment. A dental handpiece (“drill”) is used to remove large portions of decayed material from a tooth. A spoon is a dental instrument used to remove decay carefully and is sometimes employed when the decay in dentin reaches near the pulp.Once the decay is removed, the missing tooth structure requires a dental restoration of some sort to return the tooth to functionality and aesthetic condition.
Restorative materials include dental amalgam, composite resin, porcelain, and gold. Composite resin and porcelain can be made to match the color of a patient’s natural teeth and are thus used more frequently when aesthetics are a concern. Composite restorations are not as strong as dental amalgam and gold; some dentists consider the latter as the only advisable restoration for posterior areas where chewing forces are great. When the decay is too extensive, there may not be enough tooth structure remaining to allow a restorative material to be placed within the tooth. Thus, a crown may be needed. This restoration appears similar to a cap and is fitted over the remainder of the natural crown of the tooth. Crowns are often made of gold, porcelain, or porcelain fused to metal.
In certain cases, root canal therapy may be necessary for the restoration of a tooth. Root canal therapy, also called “endodontic therapy”, is recommended if the pulp in a tooth dies from infection by decay-causing bacteria or from trauma.
During a root canal, the pulp of the tooth, including the nerve and vascular tissues, is removed along with decayed portions of the tooth. The canals are instrumented with endodontic files to clean and shape them, and they are then usually filled with a rubber-like material called gutta percha. The tooth is filled and a crown can be placed. Upon completion of a root canal, the tooth is now non-vital, as it is devoid of any living tissue.
An extraction can also serve as treatment for dental caries. The removal of the decayed tooth is performed if the tooth is too far destroyed from the decay process to effectively restore the tooth. Extractions are sometimes considered if the tooth lacks an opposing tooth or will probably cause further problems in the future, as may be the case for wisdom teeth.
Extractions may also be preferred by patients unable or unwilling to undergo the expense or difficulties in restoring the tooth.
Prevention:
Oral hygiene
Personal hygiene care consists of proper brushing and flossing daily. The purpose of oral hygiene is to minimize any etiologic agents of disease in the mouth. The primary focus of brushing and flossing is to remove and prevent the formation of plaque. Plaque consists mostly of bacteria.As the amount of bacterial plaque increases, the tooth is more vulnerable to dental caries. A toothbrush can be used to remove plaque on most surfaces of the teeth except for areas between teeth.
Toothbrush are commonly used to clean teeth
When used correctly, dental floss removes plaque from areas which could otherwise develop proximal caries. Other adjunct hygiene aids include interdental brushes, water picks, and mouthwashes.
Professional hygiene care consists of regular dental examinations and cleanings. Sometimes, complete plaque removal is difficult, and a dentist or dental hygienist may be needed. Along with oral hygiene, radiographs may be taken at dental visits to detect possible dental caries development in high risk areas of the mouth.
CARIES PREVENTION IN CHILDREN- THE INDIAN CHALLENGE.
Ayurvedic Treatment & Prevention Of Tooth Decay
Homeopathic Treatment & Prevention of Tooth Decay…………..(1)………….(2).…….(3)
Dietary modification:
For dental health, the frequency of sugar intake is more important than the amount of sugar consumed. In the presence of sugar and other carbohydrates, bacteria in the mouth produce acids which can demineralize enamel, dentin, and cementum. The more frequently teeth are exposed to this environment, the more likely dental caries are to occur. Therefore, minimizing snacking is recommended, since snacking creates a continual supply of nutrition for acid-creating bacteria in the mouth.
Also, chewy and sticky foods (such as dried fruit or candy) tend to adhere to teeth longer, and consequently are best eaten as part of a meal. Brushing the teeth after meals is recommended. For children, the American Dental Association and the European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry recommend limiting the frequency of consumption of drinks with sugar, and not giving baby bottles to infants during sleep. Mothers are also recommended to avoid sharing utensils and cups with their infants to prevent transferring bacteria from the mother’s mouth.
It has been found that milk and certain kinds of cheese like cheddar can help counter tooth decay if eaten soon after the consumption of foods potentially harmful to teeth. Also, chewing gum containing xylitol (wood sugar) is widely used to protect teeth in some countries, being especially popular in the Finnish candy industry. Xylitol’s effect on reducing plaque is probably due to bacteria’s inability to utilize it like other sugars. Chewing and stimulation of flavour receptors on the tongue are also known to increase the production and release of saliva, which contains natural buffers to prevent the lowering of pH in the mouth to the point where enamel may become demineralised.
Other preventive measures:
The use of dental sealants is a good means of prevention. Sealants are thin plastic-like coating applied to the chewing surfaces of the molars. This coating prevents the accumulation of plaque in the deep grooves and thus prevents the formation of pit and fissure caries, the most common form of dental caries. Sealants are usually applied on the teeth of children, shortly after the molars erupt. Older people may also benefit from the use of tooth sealants, but their dental history and likelihood of caries formation are usually taken into consideration.
Fluoride therapy is often recommended to protect against dental caries. It has been demonstrated that water fluoridation and fluoride supplements decrease the incidence of dental caries. Fluoride helps prevent decay of a tooth by binding to the hydroxyapatite crystals in enamel. The incorporated fluoride makes enamel more resistant to demineralization and, thus, resistant to decay. Topical fluoride is also recommended to protect the surface of the teeth. This may include a fluoride toothpaste or mouthwash. Many dentists include application of topical fluoride solutions as part of routine visits.
Furthermore, recent research shows that low intensity laser radiation of argon ion lasers may prevent the susceptibility for enamel caries and white spot lesions. Also, as bacteria are a major factor contributing to poor oral health, there is currently research to find a vaccine for dental caries. As of 2004, such a vaccine has been successfully tested on non-human animals, and is in clinical trials for humans of May 2006.
Disclaimer: This information is not meant to be a substitute for professional medical advise or help. It is always best to consult with a Physician about serious health concerns. This information is in no way intended to diagnose or prescribe remedies.This is purely for educational purpose
Source:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dental_caries
![Reblog this post [with Zemanta]](https://i0.wp.com/img.zemanta.com/reblog_e.png?w=580)